Authorization Server
Keycloak is an open-source Identity and Access Management solution that provides an Authorization Server. The Authorization Server is responsible for access to resources.
TIP
See Keycloak's documentation - Authorization Services Guide for more details.
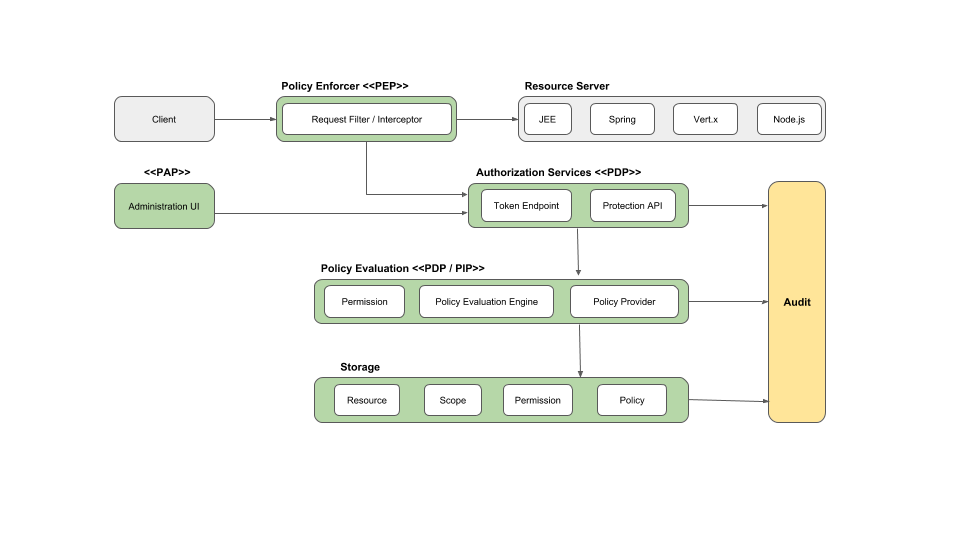
This functionality is based on a Policy Enforcement Point (PEP). The PEP is responsible for enforcing access control policies and protecting resources. It intercepts requests from clients (users) and verifies the access token before allowing or denying access to the requested resource.
By integrating Keycloak's Authorization Server and PEP into your application, you can implement fine-grained access control and secure your resources based on user roles, permissions, and other attributes.
The PEP works together with the Policy Decision Point (PDP), which is the component that actually makes the decision whether access should be granted based on the policies defined in Keycloak.
When a request to access a resource is made, the PEP intercepts the request and sends a request to the PDP to evaluate the policies associated with the requested resource. The PDP evaluates the policies and returns a decision (permit or deny) back to the PEP. The PEP then enforces this decision.
Remember that to use the PEP endpoint and the Keycloak Authorization Services, you need to enable authorization for your client in the Keycloak admin console.
TIP
See Keycloak's documentation - Authorization Server Architecture for more details.
Evaluate Permissions
Assume we have a default resource with Name "urn:test-client:resources:default".
We want to check if a given user has access to it. It is accomplished based on permissions. In our case default permission is applied to default resource type. "Default Permission" is based on policy named - "Require Admin Role". This policy checks if a user has "Admin" realm role.
Here is how to use AuthorizationBuilder to define policy for a protected resource:
services
.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddKeycloakWebApi(context.Configuration);
services
.AddAuthorization()
.AddKeycloakAuthorization()
.AddAuthorizationBuilder()
.AddPolicy(
policyName,
policy =>
policy.RequireProtectedResource(
resource: "urn:test-client:resources:default",
scope: string.Empty
)
);
services
.AddAuthorizationServer(context.Configuration)
.AddStandardResilienceHandler(); // an example of how to extend based on IHttpClientBuilder by adding PollyNOTE
The calls to Authorization Servers are made on behalf of a user based on header propagation. We are taking user's access_token (JWT Bearer Token) from IHttpContextAccessor. AddHeaderPropagation adds AccessTokenPropagationHandler delegating handler to IAuthorizationServerClient responsible for header propagation.