Protected Resources
Keycloak Authorization Server is a powerful tool that provides fine-grained access control to your services and applications. It enables developers to manage permissions and policies centrally, providing a standardized way to secure applications regardless of the platform they are built on.
Table of Contents:
Example
Let's say we have a workspace management functionality, that allows users to create and manage workspaces.
In this example, we have:
- An entity named workspace. The entity (aka resource) "my-workspace" represents a specific workspace in an application.
- The available actions on the workspace are reading and writing, represented by the scopes "workspace:read" and "workspace:write".
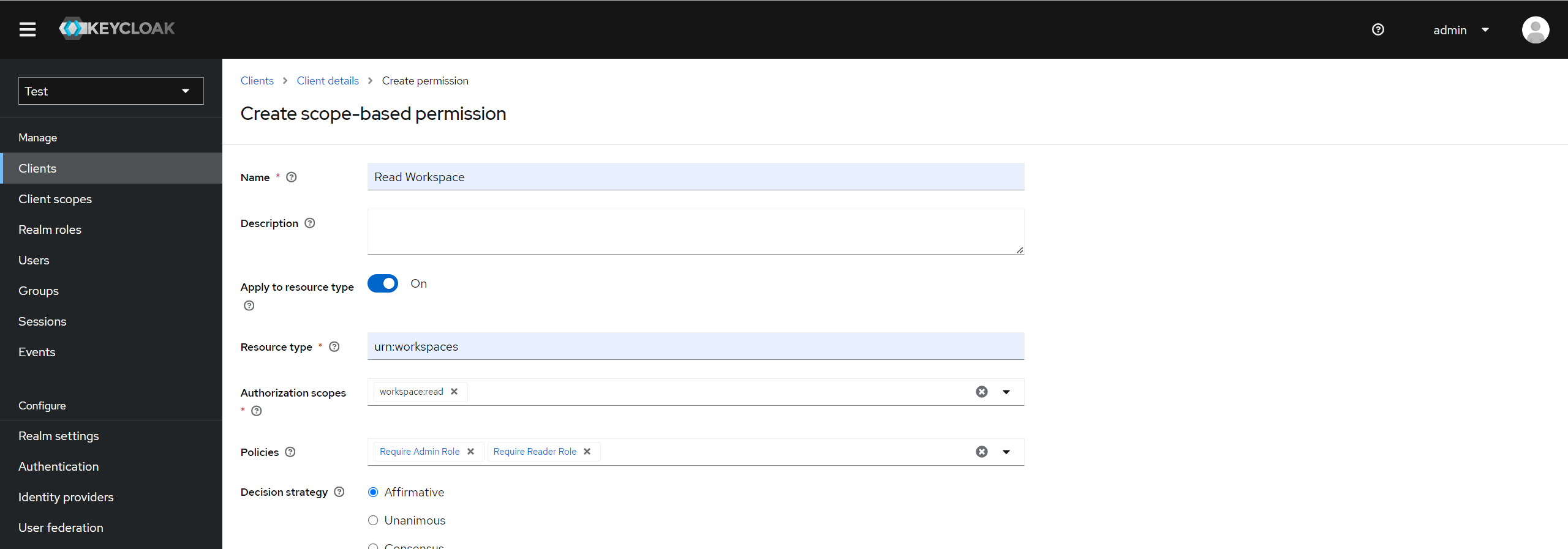
- The permissions associated with these scopes are "Read Workspace" and "Delete Workspace".
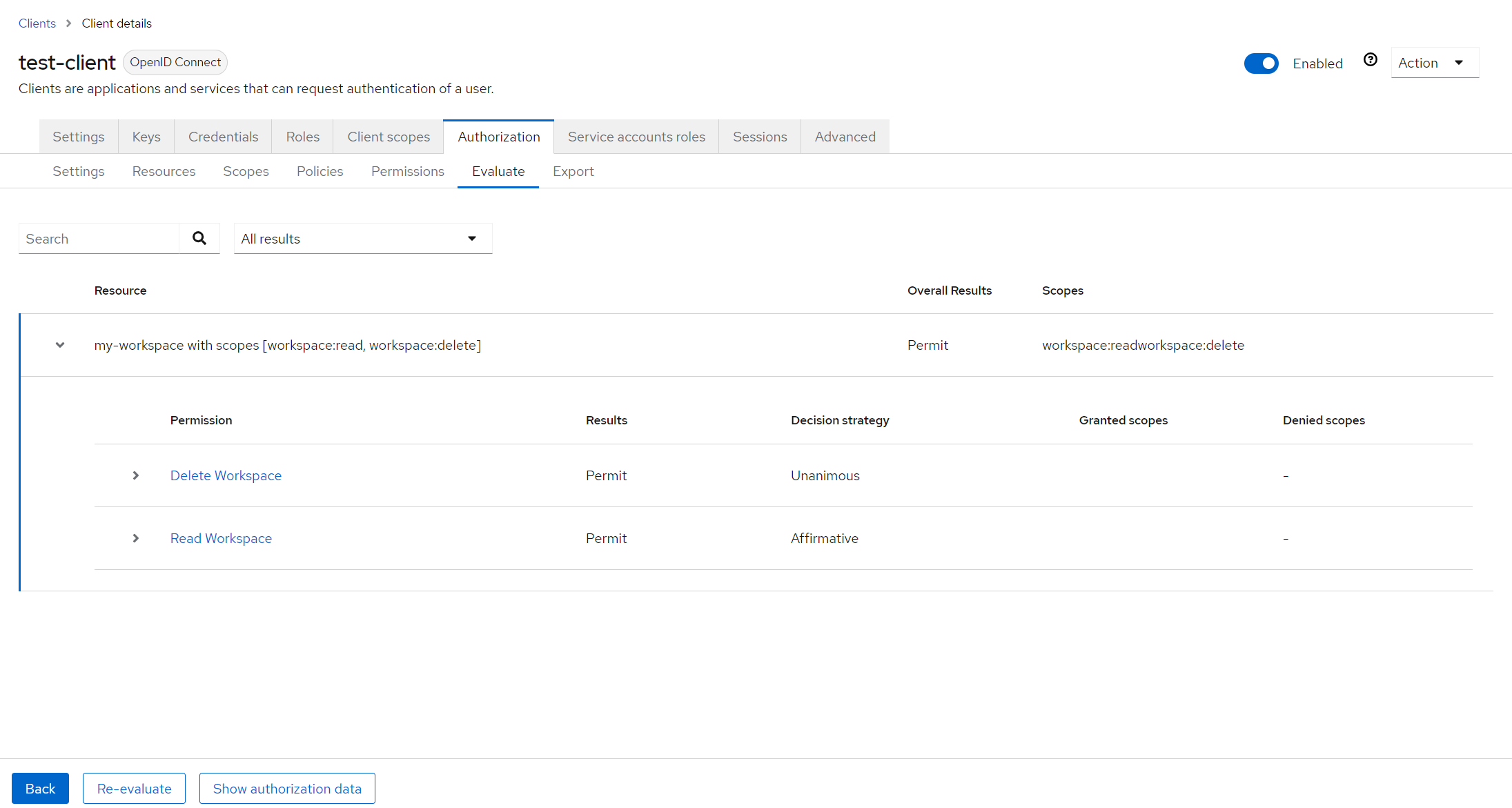
The Authorization Server evaluates these permissions to determine whether a user has access to a workspace based on their role and the requested action.
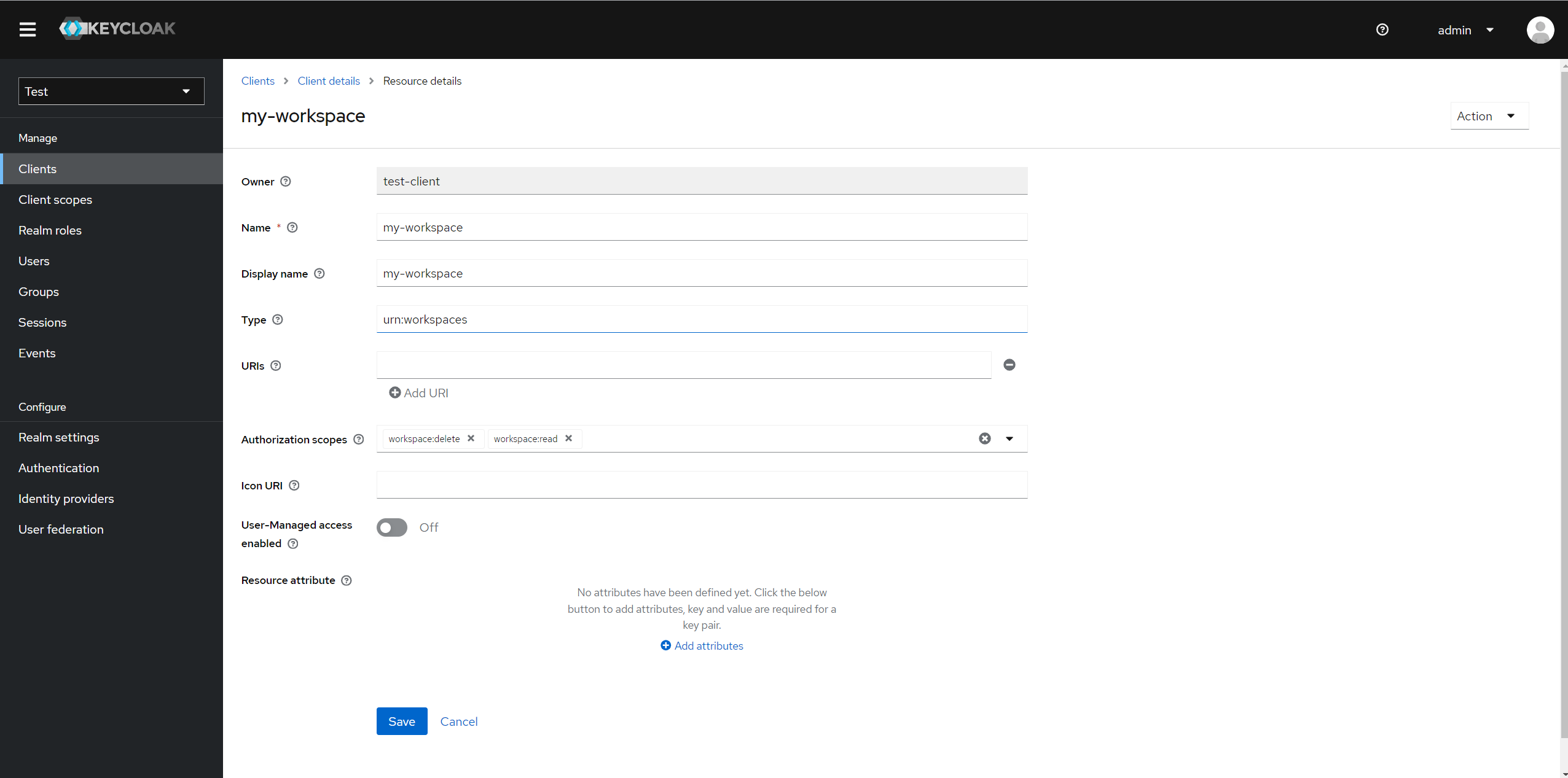
In Keycloak, you can define resources, which are the entities that you want to protect. For instance, in the given example, we have a resource named "my-workspace" with a type of "urn:workspaces". This resource could represent a workspace in an application that users can access and manipulate.
Keycloak allows you to define scopes, which are the actions that can be performed on a resource. In our example, we have two scopes defined: "workspace:read" and "workspace:write". These scopes represent the ability to read and write to the workspace.
Keycloak also allows you to define permissions, which are the rules that determine who can perform which actions on a resource. In our example, we have two permissions: "Delete Workspace" and "Read Workspace". These permissions are linked to specific scopes and are based on policies.
Policies in Keycloak are the conditions that a user must meet to be granted a permission. They can be based on various attributes, including the role of the user, time, and location.
In our example, we have two policies: "Require Admin Role" and "Require Reader Role". These policies are based on realm roles, which are roles that apply to the entire Keycloak realm.
To delete a workspace, a user must have the Admin role, as defined by the "Require Admin Role" policy. To read a workspace, a user can have either the Admin role or the Reader role, as defined by the "Require Reader Role" policy.
The Keycloak Authorization Server evaluates these policies whenever a user attempts to access a resource. If the user meets the conditions of the policy, the server grants the permission and the user can perform the action on the resource. This allows for powerful, fine-grained access control that can be easily managed and updated as your application evolves.
Configure Keycloak
NOTE
In this section, I'm not going to show you how to setup full example, but rather provide some example, for the full configuration I suggest you looking at the source code. It contains import files that Keycloak allows you to use manually or via CLI.
💡 Here an example of how to create a permission for scopes:
💡 Here is an example of how to create a resource and associate a scopes with it:
💡 Keycloak provides a UI to evaluate permissions for a given resource, user, scopes, etc. This feature enables you to prototype and troubleshoot more easily. Here is an example of how to evaluate permissions for an admin user: